Connecticut's Top-Rated 3D Printing and Scanning Services
Turn your ideas into reality with our all-in-one 3D solutions
Bringing Your Vision to Life with Cutting-Edge Technology
We offer a wide range of 3D services to bring your ideas to life. Our team of experts utilize cutting-edge technology to provide prototyping, design, visualization, and engineering solutions tailored to your unique needs at a reasonable price. Let us help turn your vision into a tangible reality.
SCHEDULE YOUR FREE CONSULTATION TODAY!
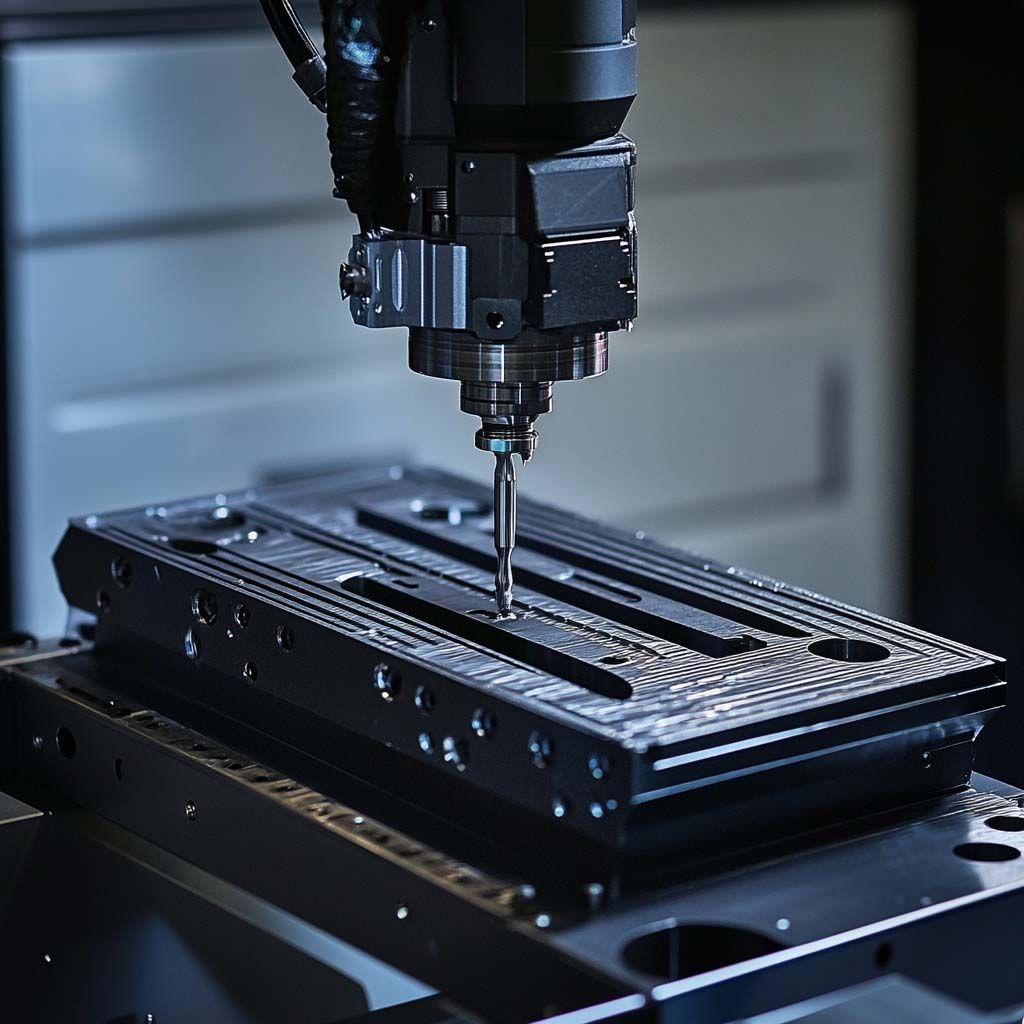

The Power of 3D Printing in Creating Fixtures for Machining and Manufacturing The world of machining and manufacturing has seen transformative technological advancements over the past few decades, and one of the most impactful innovations is 3D printing. This versatile process has revolutionized industries across the board, offering increased efficiency, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. One area where 3D printing has truly demonstrated its potential is in the creation of fixtures used in machining and manufacturing. What are Fixtures in Machining and Manufacturing? Fixtures are specialized tools or devices used to hold and support a workpiece in place while machining operations are being performed. They ensure the workpiece is positioned correctly, securely, and consistently, which is crucial for achieving precise results. Whether it’s in milling, drilling, grinding, or turning, fixtures provide the stability and repeatability needed for high-quality production. Fixtures are typically made from materials like metal or hardened steel due to the need for durability and strength. However, the traditional process of designing and creating these fixtures can be time-consuming and expensive. This is where 3D printing comes into play, offering a host of benefits that streamline the production process. The Advantages of 3D Printing for Fixtures 1. Rapid Prototyping and Design Flexibility Traditional fixture manufacturing involves designing the fixture, creating detailed drawings, and sending them to a machine shop for fabrication. This process can take weeks or even months, depending on the complexity of the fixture. In contrast, 3D printing offers rapid prototyping capabilities, allowing engineers to quickly design and produce fixtures in a matter of hours. This rapid turnaround is particularly beneficial in the early stages of production, where multiple iterations and adjustments may be required. 3D printing allows manufacturers to create and test different fixture designs, speeding up the overall development cycle and reducing time to market. 2. Cost-Effectiveness The cost of manufacturing traditional fixtures can be high, especially when complex geometries are involved. Machining these parts requires specialized tools and significant labor, which can drive up the cost. With 3D printing, however, the need for expensive tooling is eliminated. The digital nature of 3D printing means that fixtures can be produced directly from CAD files, without the need for additional setup or machine time. For low-volume runs or custom designs, 3D printing becomes an incredibly cost-effective option. 3. Customization and Complexity 3D printing opens up new possibilities in terms of fixture design complexity. Traditional manufacturing methods often struggle with intricate or non-standard geometries. However, 3D printing is ideal for producing complex shapes that would be nearly impossible or prohibitively expensive to machine. Manufacturers can create fixtures with internal channels, lattice structures, or unique contours that precisely fit the shape and needs of a particular workpiece. Customization becomes effortless, and this flexibility allows for tailored solutions that improve the overall manufacturing process. 4. Lightweight and Strong Materials With the development of advanced 3D printing materials, it’s possible to create fixtures that are both lightweight and strong enough to handle the demands of machining. Materials like high-strength plastics, carbon fiber composites, and even metal powders used in 3D printing ensure that the final fixtures can withstand heavy loads while reducing the overall weight. This is particularly advantageous in industries where fixture weight is a critical factor, such as aerospace or automotive manufacturing. Lighter fixtures also contribute to faster machine cycles, enhancing overall efficiency. 5. Reduced Lead Times and Increased Efficiency Lead time is one of the most significant challenges in traditional fixture manufacturing. From design to fabrication, the entire process can take days or even weeks. This delay can have a cascading effect on production schedules and overall factory efficiency. By contrast, 3D printing dramatically reduces lead times. Fixtures can be designed, optimized, and printed in a fraction of the time, allowing manufacturers to quickly adapt to changing production demands. In industries with tight deadlines or high-mix, low-volume production, the ability to produce fixtures quickly gives manufacturers a competitive edge. 6. Low-Volume Production and On-Demand Manufacturing One of the most compelling reasons to use 3D printing for fixtures is the ability to produce low-volume runs without the need for expensive tooling or molds. Traditional fixture production often requires significant upfront investment for high-volume runs, which may not be cost-effective for small batch sizes. 3D printing allows manufacturers to produce fixtures on-demand and in small quantities, which is ideal for industries where the need for specialized or custom fixtures is infrequent. This on-demand capability reduces waste and optimizes resource allocation. 7. Reduced Waste and Sustainability Traditional machining methods often generate significant amounts of material waste due to the subtractive nature of the process. With 3D printing, material is only added where needed, minimizing waste and reducing the environmental impact. Additionally, many 3D printing materials are recyclable, contributing to a more sustainable production process. As industries continue to prioritize sustainability, 3D printing offers an eco-friendly alternative to traditional manufacturing methods. Real-World Applications of 3D Printed Fixtures The benefits of 3D printing for fixtures are already being realized in various industries: Aerospace : Aerospace companies use 3D printed fixtures to hold complex components in place during assembly, reducing weight and improving precision. Lightweight, durable fixtures are essential in this highly demanding industry. Automotive : In automotive manufacturing, 3D printed fixtures are used for custom parts that require precise alignment during machining. The ability to produce low-volume, highly specialized fixtures at a lower cost has a significant impact on overall production efficiency. Medical : In medical device manufacturing, custom fixtures are necessary to handle delicate and intricate parts. 3D printing allows for the rapid production of these custom tools, ensuring both precision and cost savings. Tooling and Prototyping : Industries focused on prototyping benefit from 3D printed fixtures to secure prototype parts in place for testing and analysis. The ability to quickly create multiple fixture variations speeds up the overall prototyping process. Conclusion 3D printing has emerged as a game-changer in the world of machining and manufacturing, particularly when it comes to the creation of fixtures. With its ability to offer rapid prototyping, cost-effective production, customization, and sustainability, 3D printing is reshaping how manufacturers approach fixture design and production. As industries continue to embrace this technology, the future of manufacturing will undoubtedly be more flexible, efficient, and cost-effective, with 3D printing playing a pivotal role in shaping the way fixtures are created and used. By integrating 3D printing into their operations, manufacturers can unlock new levels of productivity, reduce costs, and enhance their overall ability to innovate.

How Rev3D Services Can Help You Develop Your Idea into a Manufactured Product Turning a brilliant idea into a tangible product can be an exciting yet overwhelming process. Whether you're an entrepreneur with a new invention or a business looking to innovate, having the right support to guide you from concept to manufactured product is essential. At Rev3D, we specialize in helping you transform your idea into a fully realized, market-ready product with expert product development and manufacturing services. In this blog, we’ll walk you through how Rev3D’s services can help you take your idea from inception to production, ensuring that it not only looks great but functions flawlessly. 1. Initial Consultation and Idea Refinement Every great product starts with a spark of inspiration, but that spark needs to be refined into a clear, viable concept. At Rev3D, we begin by sitting down with you to discuss your idea, your goals, and your vision for the product. We help you clarify your concept and ensure that it is well-defined, so we can start working on the details that will make it a reality. Understanding Your Needs: Whether it’s a new product design, a functional improvement, or a full innovation, we listen carefully to understand your exact requirements and how we can best serve you. Feasibility Assessment: We help you assess the technical feasibility of your idea, ensuring that it’s realistic and practical to produce. This stage is crucial to identifying any early challenges or opportunities. By refining your concept early on, we ensure that we are aligned in every step of the development process, reducing any risks as we move forward. 2. Design and Prototyping: Bringing Your Idea to Life With a clear idea in mind, the next step is to create a design that works. Our design team at Rev3D is skilled in turning abstract concepts into detailed 3D models, drawings, and prototypes that allow you to see and interact with your product before manufacturing even begins. 3D Modeling: Using advanced CAD software, we create detailed 3D models of your product, ensuring that it looks, functions, and feels just as you envisioned. Prototyping: We then move on to rapid prototyping, creating physical models or functional prototypes using 3D printing, CNC machining, or other methods, depending on your product’s material and complexity. Prototyping is a key phase that allows you to evaluate the design, identify any design flaws, and make adjustments before production begins. It’s a critical opportunity to refine your product and ensure it meets your expectations. 3. Engineering and Development: Ensuring Functionality and Feasibility Designing a product is one thing, but ensuring that it works as intended is where Rev3D truly excels. We provide comprehensive engineering and development services that ensure your product isn’t just well-designed—it’s engineered for performance, durability, and manufacturability. Engineering Optimization: Our engineering team looks at the design from a technical perspective, making sure that it can be manufactured efficiently and meets all necessary standards. Material Selection: We guide you through the process of selecting the right materials for your product, balancing cost, durability, and functionality to ensure that it performs as intended. Design for Manufacturability (DFM): We make sure that your design is not only functional but also optimized for mass production. This includes simplifying complex features, reducing material waste, and ensuring that your product can be assembled with minimal labor. With our engineering expertise, we ensure that your product isn’t just a concept—it’s a fully functional and manufacturable product. 4. Manufacturing: From Prototype to Production Once the design and engineering are complete, the next step is to bring your product to life on a larger scale. At Rev3D, we provide end-to-end manufacturing solutions to ensure your product is produced efficiently, consistently, and to the highest quality standards. Manufacturing Setup: Whether you need low-volume production or large-scale manufacturing, we help set up the production process, including sourcing materials and selecting the best manufacturing methods (e.g., injection molding, CNC machining, or additive manufacturing). Production Run: We oversee the entire manufacturing process, ensuring everything runs smoothly from the initial production run to the final product. Our team works closely with manufacturers to monitor quality, timelines, and costs. Quality Control: Quality assurance is a top priority at Rev3D. We implement rigorous testing protocols to ensure that your product meets all performance, safety, and regulatory standards before it goes to market. With our expertise, your idea will seamlessly transition from a prototype to a high-quality, mass-produced product ready for the market. Why Choose Rev3D? Rev3D is more than just a product development company—we’re your trusted partner in turning your idea into a successful, manufactured product. Here’s why working with us makes all the difference: End-to-End Expertise: From concept to delivery, we handle every stage of the product development and manufacturing process, ensuring a seamless transition at every step. Customization: We tailor our services to meet the specific needs of your product, offering flexible solutions that align with your goals and timeline. Quality and Precision: Our attention to detail and commitment to quality ensure that your product meets the highest standards in design, performance, and durability. Conclusion: Let Rev3D Help You Turn Your Idea Into a Reality At Rev3D, we’re dedicated to helping you transform your ideas into real, market-ready products. Whether you’re at the initial concept stage or ready to scale up production, our team of experts will guide you through every step of the process—from design and prototyping to manufacturing and logistics. If you’re ready to take your idea to the next level, contact Rev3D today. Let’s bring your vision to life and create a product that stands out in the marketplace!

Creating a new product is an exciting but complex journey. From initial idea to market launch, product development involves a series of stages that ensure a smooth transition from concept to customer. Understanding each stage is essential whether you're an entrepreneur, a startup, or part of an established company looking to innovate. In this blog, we'll break down the stages of product development into clear, actionable steps to help you navigate the entire process. 1. Idea Generation & Discovery Every product starts with a spark—an idea. The first stage of product development is all about identifying opportunities, solving problems, or discovering unmet market needs. Key Activities: Brainstorming: Gather your team or stakeholders to generate creative and innovative ideas. Identifying Market Needs: Look for gaps in the market or consumer pain points that your product could address. Research Competitors: Understand what competitors are offering and identify ways to improve or differentiate your solution. Customer Feedback: Reach out to potential customers to understand their needs and preferences. Questions to Ask: What problem does this product solve? Who will benefit from this product? What makes this idea unique or better than competitors? 2. Idea Screening & Feasibility Analysis Not every idea will make it through the development process. The next stage involves screening your ideas for feasibility, potential, and alignment with your goals. Key Activities: Screening Ideas: Prioritize ideas based on their market potential, cost, risk, and alignment with your company goals. Technical Feasibility Analysis: Assess whether your idea can be developed with the available technology or expertise. Financial Feasibility: Estimate costs, return on investment (ROI), and determine if the product is financially viable. Market Research: Analyze trends, customer needs, and demand to verify market opportunities. Questions to Ask: Can we realistically build this product? Does this idea align with our target market and mission? How much will this cost, and can we expect a profitable return? 3. Concept Development & Design Once you've screened your idea and confirmed feasibility, it's time to flesh it out. The concept development stage focuses on creating detailed plans and defining the design and features of your product. Key Activities: Define Product Features: Determine what the product will include and how it will solve the identified problem. Design & Prototyping: Create sketches, models, and digital representations to visualize the product's functionality. User Experience (UX) Design: Ensure the design is intuitive, functional, and meets customer needs. Technical Planning: Establish technical requirements and select tools or technology necessary for development. Tools Commonly Used: CAD Software (e.g., AutoCAD, SolidWorks) Wireframing Tools (e.g., Figma, Adobe XD) Prototyping Tools (e.g., 3D printing, mock-ups) 4. Prototype Development & Testing With a concept in mind, the next stage is to create a prototype —a working model of your product. Prototyping allows you to evaluate your design, functionality, and user experience before investing heavily in production. Key Activities: Build the Prototype: Create a physical or digital prototype that represents your idea. Test Functionality: Ensure the prototype works as intended and solves the customer problem. User Testing: Allow real users to interact with your prototype to gather feedback. Iterate & Refine: Based on testing feedback, refine the design and functionality. Why Prototyping is Crucial: Detect design flaws or functional issues early. Save time and costs by addressing problems during testing rather than during full-scale production. Improve user experience by incorporating real customer feedback. 5. Product Development & Manufacturing After the prototype has been thoroughly tested and adjusted, the next step is scaling production. This stage is about transitioning from testing to mass production while maintaining quality standards. Key Activities: Design for Manufacturing (DFM): Adapt designs to ensure they are easy and cost-effective to manufacture. Select a Production Method: Choose between in-house production or outsourcing to a manufacturer. Sourcing Materials: Identify suppliers, negotiate contracts, and ensure the timely delivery of necessary materials. Setup Production Lines: Establish assembly processes, quality checks, and timelines for large-scale production. 6. Market Testing & Validation Before fully launching your product, it's important to test its reception in the market. Market testing allows you to gather insights and data about how well your product will perform with your target audience. Key Activities: Pilot Testing: Test the product with a smaller group of customers or target markets. Beta Programs: Offer limited access to early adopters for feedback. Gather Feedback: Identify any issues, customer preferences, or additional features to consider. Adjustments: Based on feedback, fine-tune the product or marketing strategy. Why Market Testing Matters: Avoid costly mistakes by identifying potential product flaws or misalignment with customer needs. Build confidence by demonstrating customer demand and feedback. 7. Product Launch & Commercialization After successful testing and development, you're ready to introduce your product to the market. This stage involves marketing, promotion, distribution, and ensuring that consumers can access and use your product. Key Activities: Develop a Go-to-Market Strategy: Plan how you'll introduce your product to customers. Create a Marketing Plan: Establish promotional strategies using digital ads, social media, PR campaigns, content marketing, and partnerships. Distribute the Product: Choose effective distribution channels—retail, e-commerce, or direct-to-consumer options. Customer Support & Feedback: Set up post-launch support and monitor customer feedback for future updates. 8. Post-Launch Review & Maintenance Even after your product is launched, your work isn't over. This final stage involves monitoring performance, gathering customer feedback, and addressing any issues post-launch. Key Activities: Track Sales & Performance Metrics: Monitor KPIs like customer adoption rates, churn rates, and reviews. Customer Support: Ensure customer satisfaction by resolving complaints, issues, or concerns. Iterate on the Product: Improve the product based on data and feedback to address market needs over time. Plan for Updates: Introduce updates, new features, or improvements to keep customers engaged. Final Thoughts: Product Development is an Ongoing Journey Product development isn’t just about creating and launching one product. It's a cycle of ideation, design, testing, feedback, and innovation. Once you launch, the goal should be to continually improve and adapt based on market changes and consumer needs. By understanding these stages of product development, you position yourself for a smoother, more strategic journey—reducing risks, optimizing resources, and increasing your product's chances of success. Now that you know the steps, are you ready to bring your product idea to life? The first step is to start with clarity, research, and a plan. Good luck! 🚀

How 3D Printing, Scanning, and Engineering Work Together to Optimize Product Design In today’s fast-paced product development environment, businesses are increasingly turning to advanced technologies to streamline design processes, reduce costs, and enhance product quality. One powerful combination of tools—3D printing, 3D scanning, and engineering—works synergistically to accelerate product development and optimize design. In this article, we’ll delve into how these technologies complement each other, creating a seamless workflow that brings products from concept to market faster and more efficiently. 1. 3D Scanning: Capturing the Physical World The journey of product design often begins with a physical object or prototype, and this is where 3D scanning plays a critical role. By using high-precision laser or structured light scanning technologies, engineers can quickly capture the exact dimensions and geometries of existing parts or prototypes. This digitization of the physical object allows for detailed analysis and modification without needing to manually measure or recreate the part. 3D scanning is particularly valuable in reverse engineering, where a physical part needs to be reproduced or improved. Whether you’re looking to recreate a legacy part, improve a design, or adapt an existing component for a new application, scanning provides an accurate digital blueprint. This data can then be fed directly into CAD (computer-aided design) software, facilitating an easy transition from the physical to the digital realm. 2. 3D Printing: Bringing Designs to Life Once the initial designs have been scanned or conceptualized, 3D printing comes into play. Additive manufacturing (3D printing) allows designers to rapidly create prototypes or even final products directly from digital models. This flexibility speeds up iteration cycles and allows for real-time modifications and testing. For product design, 3D printing is particularly useful in producing complex geometries and structures that would be impossible or prohibitively expensive with traditional manufacturing methods. Designers can experiment with lightweight, intricate, or organic shapes without the limitations of conventional tools. In addition, 3D printing allows for the production of small batches or custom products, making it a versatile solution for both prototyping and low-volume manufacturing. The iterative process enabled by 3D printing is one of its greatest strengths. Designers can test the fit, function, and form of a product early in the design phase, receiving real-world feedback that can be used to refine the design. This “fail fast” approach ultimately leads to better products and faster development times. 3. Engineering: The Backbone of Optimization While 3D scanning and printing provide the tools for rapid iteration and prototyping, it’s engineering that ensures the product will meet performance standards, durability requirements, and manufacturing constraints. Mechanical engineers take the digital models produced through 3D scanning and printing and apply rigorous simulations, testing, and optimization techniques to ensure the final design performs as expected. Through techniques like finite element analysis (FEA) and computational fluid dynamics (CFD), engineers can simulate how a product will behave under real-world conditions. These analyses help identify weak points in the design, suggest material changes, or recommend structural adjustments to improve performance. Engineering also plays a key role in ensuring that designs are manufacturable at scale, whether using 3D printing or more traditional manufacturing methods. In many cases, engineers also collaborate with industrial designers to ensure that the product not only functions well but also appeals to the end user. By combining technical expertise with design sensibility, engineers optimize products for both usability and manufacturability. The Synergy Between 3D Scanning, Printing, and Engineering The real power of 3D scanning, printing, and engineering lies in how these technologies work together to create a streamlined product development process. 3D scanning provides the foundation by converting physical objects into precise digital models. Once the digital model is ready, 3D printing enables rapid prototyping and iteration, allowing designers to quickly test ideas and make changes. Finally, engineering ensures that the product will perform optimally by applying simulations and analyses, addressing potential issues before the product is finalized for production. This synergy allows for shorter development cycles, reduced costs, and higher-quality products. By seamlessly moving between physical and digital realms, businesses can ensure that their products meet both functional and aesthetic goals while remaining within budget and production timelines. Conclusion The integration of 3D scanning, 3D printing, and engineering has fundamentally changed how products are designed and developed. By leveraging the strengths of each technology, product designers and engineers can optimize designs, reduce time-to-market, and bring innovative products to life. Whether you're developing a new product from scratch, improving an existing one, or customizing a solution for a specific client, the combined power of these tools offers unmatched flexibility and efficiency in today’s competitive marketplace.
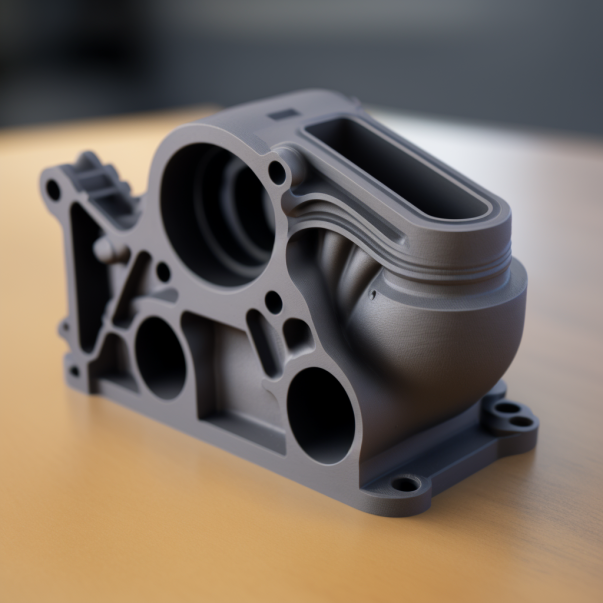
In the realm of product development, functional prototypes play a crucial role in testing and refining new designs. They provide a tangible way to evaluate a product's form, fit, and function before mass production. One of the most innovative methods for creating these prototypes is 3D printing. At Rev 3D Services, based in Connecticut, we specialize in leveraging advanced 3D printing technologies to produce high-quality functional prototypes for various industries, including those in Fairfield County and New Haven County. This article explores how 3D printing can be effectively used to create functional prototypes. What is a Functional Prototype? A functional prototype is a working model of a product used to test and validate its design and functionality. Unlike aesthetic prototypes, which focus solely on appearance, functional prototypes are meant to replicate the mechanical and operational aspects of the final product. They are critical for identifying potential design flaws, assessing usability, and ensuring the product meets all required specifications. How Does 3D Printing Enable Functional Prototyping? 3D printing offers several advantages for creating functional prototypes, making it an ideal choice for product developers and engineers. Here’s how 3D printing facilitates functional prototyping: Material Versatility: 3D printing supports a wide range of materials, including durable plastics, metals, and flexible materials. This variety allows the creation of prototypes that can closely mimic the properties of the final product. Complex Geometries: Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, 3D printing can produce complex geometries and intricate designs. This capability enables the creation of prototypes with detailed features, internal structures, and moving parts. Rapid Iteration: The speed of 3D printing allows for quick production of prototypes, enabling rapid iteration and testing. This is particularly beneficial in the early stages of product development when multiple design changes are common. Cost-Effective: 3D printing eliminates the need for expensive molds and tooling, making it a cost-effective solution for producing functional prototypes, especially in small quantities. Customization: 3D printing offers unparalleled flexibility for customization, allowing developers to create prototypes tailored to specific requirements and modifications. Types of 3D Printing Technologies for Functional Prototyping Different 3D printing technologies are suitable for creating functional prototypes, each offering unique benefits: Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): Ideal for producing strong and durable prototypes. FDM is commonly used for mechanical parts and functional assemblies. Stereolithography (SLA): Known for its high-resolution output, SLA is suitable for creating detailed prototypes with smooth surfaces, often used in medical and dental applications. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): Utilizes powdered materials to create highly durable prototypes. SLS is perfect for producing complex, functional parts with excellent mechanical properties. Digital Light Processing (DLP): Similar to SLA but with faster build times, DLP is ideal for detailed and intricate prototypes that require high precision. Applications of Functional Prototypes in Various Industries Functional prototypes created through 3D printing are invaluable across multiple industries: Automotive: Prototyping engine components, testing aerodynamic properties, and developing custom parts. Medical and Healthcare: Creating custom surgical instruments, prosthetics, and anatomical models for testing and training. Consumer Electronics: Designing and testing new gadgets, housings, and electronic components. Aerospace: Developing lightweight components, testing structural integrity, and producing custom tools. Rev 3D Services: Your Partner for Functional Prototypes At Rev 3D Services, we pride ourselves on delivering top-tier 3D printing services to create functional prototypes that meet your specific needs. Our advanced printing technologies and skilled team ensure that each prototype accurately represents your design, offering valuable insights into its functionality and performance. Why Choose Rev 3D Services? Expertise: Extensive experience in producing functional prototypes for various industries. Quality: Commitment to high-quality materials and precise manufacturing. Local Support: Conveniently located in Connecticut, serving Fairfield County, New Haven County, and surrounding areas. Conclusion 3D printing has revolutionized the process of creating functional prototypes, providing a versatile, cost-effective, and efficient solution for product development. Whether you're an entrepreneur looking to bring a new product to market or an established company seeking to refine an existing design, Rev 3D Services in Connecticut is your trusted partner. Contact us today to learn how we can assist with your functional prototyping needs.
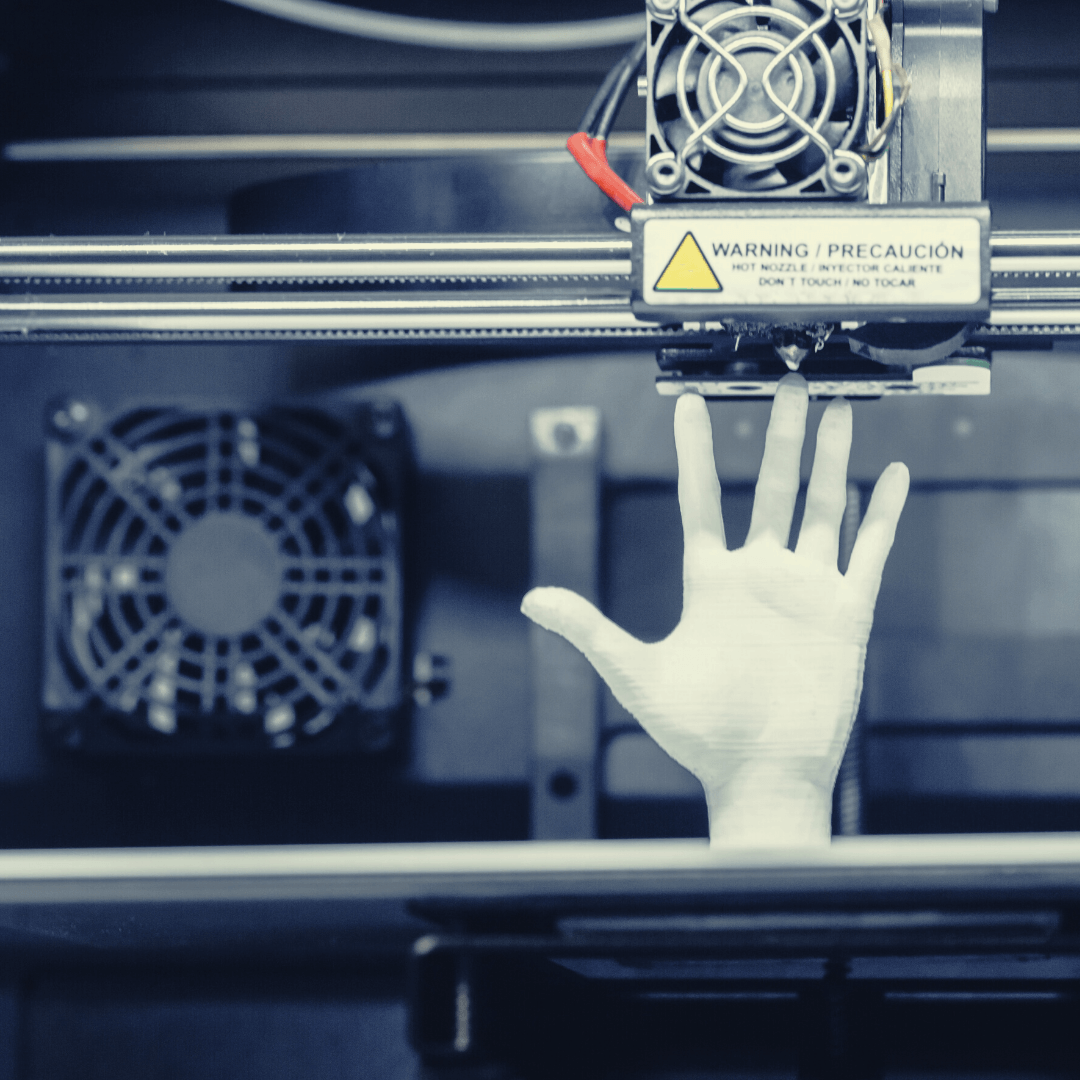
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has revolutionized various industries by offering innovative solutions that traditional manufacturing methods can't match. From creating complex geometries to rapid prototyping, 3D printing has become a cornerstone of modern production. Rev 3D Services, based in Connecticut, proudly serves Fairfield County, New Haven County, and beyond, offering cutting-edge 3D printing solutions tailored to diverse industries. In this article, we'll explore the industries that benefit the most from 3D printing and how it transforms their processes. 1. Healthcare and Medical The healthcare and medical industry has seen significant advancements thanks to 3D printing. The technology enables the creation of custom prosthetics, implants, and surgical guides, tailored to individual patient needs. 3D printing allows for the precise replication of anatomical structures, enhancing surgical accuracy and patient outcomes. Additionally, the ability to produce on-demand medical devices reduces costs and waste. Applications: Custom prosthetics and orthotics Surgical instruments and guides Dental implants and models Anatomical models for medical training 2. Aerospace and Defense The aerospace and defense industries require components that are both lightweight and durable. 3D printing excels in producing complex, high-strength parts while reducing material waste. This technology enables the manufacturing of components with intricate geometries that are challenging to achieve through traditional methods. As a result, 3D printing helps optimize performance and efficiency in aerospace applications. Applications: Lightweight structural components Complex engine parts Custom tooling and fixtures Prototyping and testing models 3. Automotive Industry The automotive industry benefits from 3D printing in numerous ways, from rapid prototyping to the production of end-use parts. The ability to quickly iterate designs and test prototypes accelerates the development process. Additionally, 3D printing allows for the customization of interior and exterior components, catering to consumer preferences and special needs. Applications: Prototyping and design validation Custom interior and exterior parts Manufacturing tools and jigs Spare parts and aftermarket components 4. Consumer Goods and Retail 3D printing has made significant inroads into the consumer goods and retail sectors, offering personalized products and reducing time-to-market. From fashion accessories to home decor, 3D printing allows businesses to offer unique, customized items. The technology also facilitates small-scale production, making it ideal for startups and niche markets. Applications: Customized jewelry and accessories Home decor and furniture Personalized gadgets and electronics Small-scale production and prototyping 5. Education and Research The education and research sectors benefit immensely from 3D printing, which provides a hands-on learning experience and facilitates the exploration of complex concepts. Educational institutions use 3D printers to teach students about design, engineering, and material sciences. Researchers employ the technology to develop prototypes, models, and specialized equipment for experiments. Applications: Educational models and kits Research prototypes and experiments Specialized lab equipment Student projects and competitions 6. Architecture and Construction In the architecture and construction industries, 3D printing offers innovative solutions for creating detailed models, prototypes, and even building components. The ability to produce scale models allows architects and designers to visualize projects better and communicate their ideas to clients. Additionally, 3D printing can create custom building components, reducing construction time and costs. Applications: Architectural models and prototypes Custom building components Decorative elements and facades Sustainable building solutions Rev 3D Services: Your Connecticut 3D Printing Partner At Rev 3D Services, we specialize in providing comprehensive 3D printing solutions across Fairfield County, New Haven County, and other areas in Connecticut. Our state-of-the-art facilities and expert team are dedicated to delivering high-quality, customized 3D printing services to meet the unique needs of various industries. Why Choose Rev 3D Services? Expertise: Our experienced team offers tailored solutions for complex projects. Quality: We use advanced 3D printing technologies to ensure precision and durability. Flexibility: We cater to a wide range of industries, providing customized services. Local Presence: Proudly serving Fairfield and New Haven counties, we are your local 3D printing experts. 3D printing has revolutionized multiple industries by offering unparalleled customization, rapid prototyping, and cost-effective manufacturing solutions. Whether you're in healthcare, aerospace, automotive, or another field, Rev 3D Services in Connecticut is here to help you harness the power of 3D printing. Contact us today to learn how we can assist with your next project.
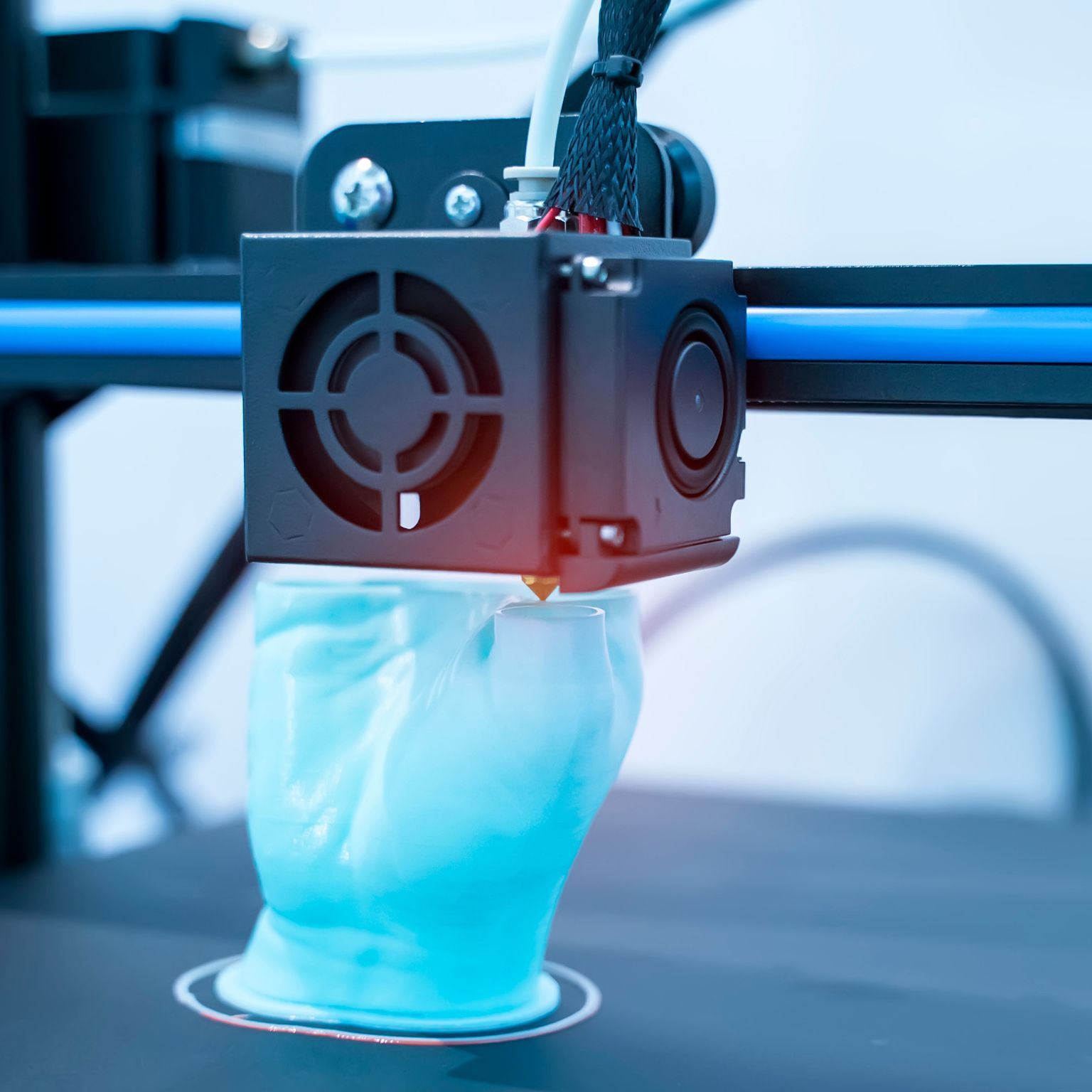

In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, 3D printing has emerged as a revolutionary force, transforming industries and sparking innovation across the globe. From creating intricate prototypes to producing functional end-use parts, 3D printing has reshaped how we think about manufacturing and design. At Rev 3D Services, we specialize in harnessing this technology's power to bring your ideas to life. But what exactly is 3D printing, and how does it work? Let's delve into the fascinating world of additive manufacturing. What is 3D Printing? 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects from a digital file. Unlike traditional methods that involve subtractive processes, 3D printing builds objects layer by layer, adding material only where needed. This method offers unparalleled flexibility, enabling complex geometries and custom designs. The concept of 3D printing dates back to the 1980s with the advent of stereolithography. Over the years, advancements in technology and materials have made 3D printing more accessible and versatile. Today, it encompasses various technologies, each offering unique benefits for different applications. How Does 3D Printing Work? The 3D printing process starts with a digital 3D model, typically created using computer-aided design (CAD) software. This model is sliced into thin horizontal layers, which guide the printer in building the object. Here's a step-by-step breakdown: Design Creation: Create a 3D model using CAD software or by scanning an existing object. File Preparation: Convert the model into a printer-friendly format, usually STL (Standard Tessellation Language). Slicing: The STL file is sliced into thin layers, generating instructions for the printer. Printing: The printer follows the instructions to deposit material layer by layer. Post-Processing: Depending on the material and technology, the object may require additional steps such as curing, polishing, or painting. Types of 3D Printing Technologies Several 3D printing technologies cater to various applications: Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): Utilizes a thermoplastic filament, heated and extruded to form layers. Popular for prototyping due to its affordability. Stereolithography (SLA): Uses a laser to cure liquid resin into solid layers, ideal for high-resolution, smooth-surfaced models. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): Employs a laser to fuse powdered materials like nylon or metals, suitable for durable, functional parts. Digital Light Processing (DLP): Similar to SLA, using a digital light projector for faster printing and detailed results. Other Technologies: Include Metal Printing, Multi Jet Fusion, and more, each with unique applications. Applications of 3D Printing 3D printing applications span across numerous industries: Medical and Healthcare: Custom implants, prosthetics, and surgical guides. Automotive and Aerospace: Lightweight components and custom parts. Prototyping and Manufacturing: Accelerated development and testing of new designs. Art and Design: Creative sculptures, jewelry, and home decor. Customization and Consumer Products: Personalized items such as phone cases and accessories. Benefits of 3D Printing The benefits of 3D printing include: Cost-Efficiency: Reduced material waste and tooling costs. Customization: Tailor-made products and components. Rapid Prototyping: Speed up the design and development process. Sustainability: Minimize waste and enable eco-friendly materials. Rev 3D Services' Offerings At Rev 3D Services, we offer comprehensive 3D printing solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our services include: High-resolution SLA and DLP printing Durable SLS and FDM parts Custom design and CAD modeling Post-processing and finishing services Our portfolio showcases successful projects across various industries, demonstrating our versatility and commitment to quality. From custom prosthetics to intricate sculptures, we've helped clients turn their visions into reality. Conclusion 3D printing has revolutionized the way we approach design and manufacturing, offering unprecedented flexibility and efficiency. At Rev 3D Services, we are dedicated to using this technology to meet your specific needs and bring your ideas to life. Whether you're an entrepreneur, artist, or engineer, our comprehensive range of services ensures that your project is in capable hands. Ready to explore the possibilities of 3D printing? Contact Rev 3D Services today for a consultation and let us help you turn your ideas into tangible reality.







